To estimate the possible horsepower (HP) a fuel injector can support, you can use the following formula:
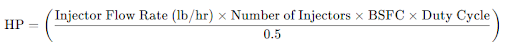
Where:
- Injector Flow Rate (lb/hr): Fuel injector size, usually rated in pounds per hour (lb/hr) at a specified fuel pressure.
- Number of Injectors: Total number of injectors in the engine.
- BSFC (Brake Specific Fuel Consumption): Typical values:
- Naturally aspirated engines: 0.45 to 0.55 lb/hr/HP
- Forced induction (turbo/supercharged) engines: 0.55 to 0.65 lb/hr/HP
- Duty Cycle: The percentage of injector operation time, typically set to a safe limit (80-85%) to avoid overworking injectors.
- 0.5: A conversion factor to account for fuel’s energy content in gasoline engines.
Step-by-Step Calculation Example:
Given Data:
- Injector size: 42 lb/hr
- Number of injectors: 8
- BSFC: 0.50 (for naturally aspirated engine)
- Duty cycle: 85% (0.85)
Calculation:
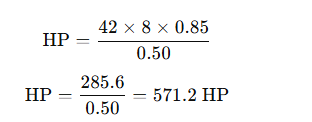
Thus, with these injectors, the engine could potentially support around 570 HP.
Additional Considerations:
- Fuel Pressure: Increasing fuel pressure can allow injectors to flow more fuel, but the injectors must be rated for the higher pressure.
Fuel Type: The formula assumes gasoline; different fuels (e.g., E85, methanol) require different BSFC values.
Safety Margin: It’s recommended to select injectors that provide some overhead to avoid running them at max duty cycle.
